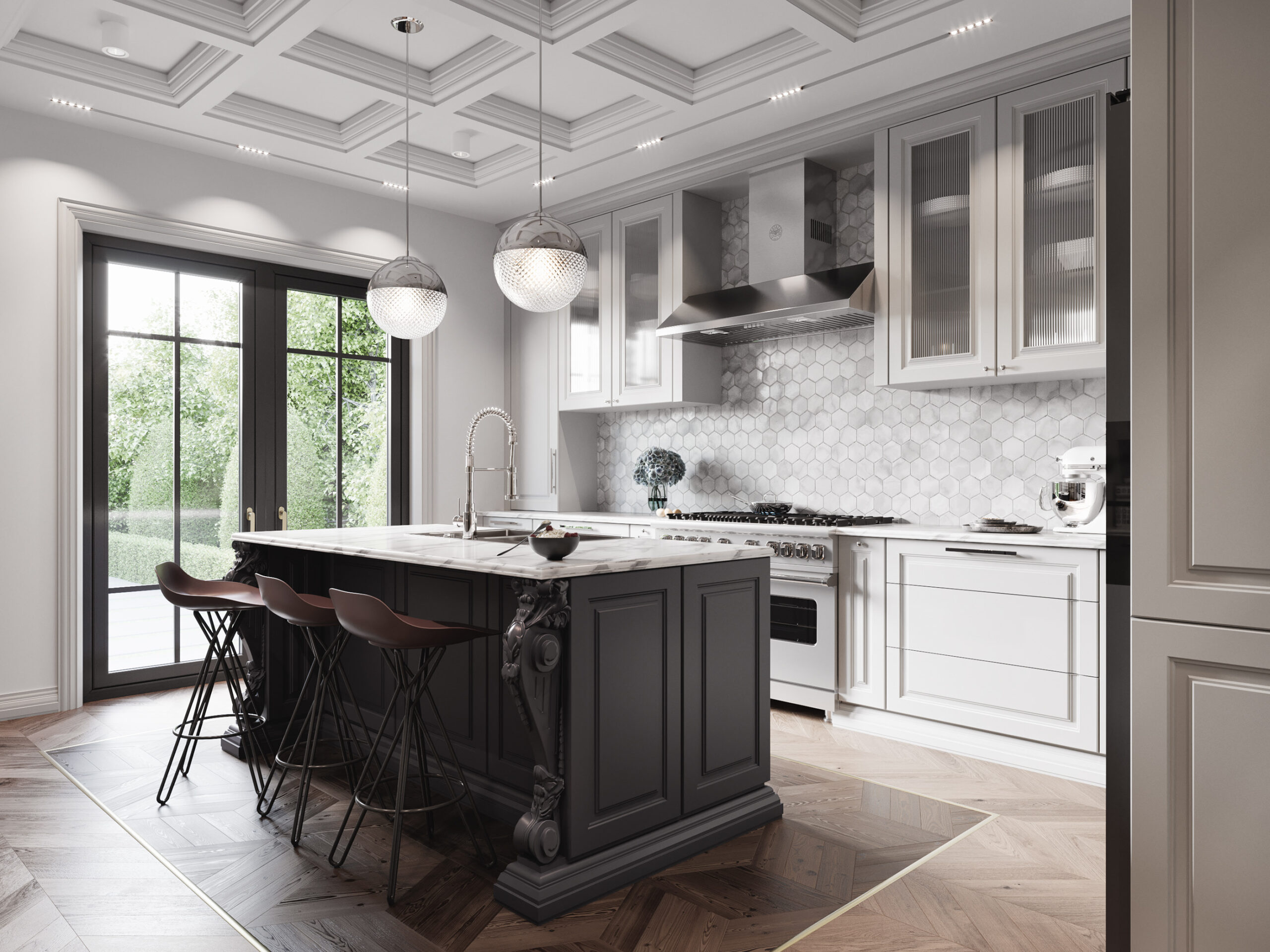
Choosing kitchen furniture carefully depends significantly on the raw materials used, as these materials impact the appearance, durability, and ease of maintenance. As an architectural expert, here’s a comprehensive guide focusing primarily on the available raw materials, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
1. Types of Raw Materials Used in Kitchen Furniture
1.1 Natural Wood
- Common Types: Oak, beech, walnut.
- Advantages:
- Luxurious and warm appearance.
- Durable and long-lasting.
- Can be refinished and restored.
- Disadvantages:
- High cost.
- Susceptible to moisture unless treated.
- Usage:
- Cabinet doors and decorations for rustic or classic kitchens.
1.2 Engineered Wood
- MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard):
- Advantages:
- Smooth surface suitable for various finishes (paints, laminates).
- Lower cost compared to natural wood.
- Disadvantages:
- Less durable when exposed to water.
- Prone to damage under heavy loads.
- Advantages:
- HDF (High-Density Fiberboard):
- More dense and water-resistant than MDF.
- Plywood:
- Composed of compressed layers, providing greater durability and stability.
1.3 Metals
- Common Types: Stainless steel, aluminum.
- Advantages:
- Excellent resistance to moisture and rust.
- Highly durable and easy to clean.
- Suitable for modern designs and commercial kitchens.
- Disadvantages:
- Can feel cold and less inviting in home kitchens.
- Higher cost compared to some other materials.
1.4 Glass
- Usage:
- Cabinet doors, countertops, shelves.
- Advantages:
- Modern and elegant appearance.
- Easy to clean.
- Disadvantages:
- Prone to breakage.
- Requires consistent maintenance to stay clean.
1.5 Natural and Artificial Stones
- Marble and Granite:
- Advantages:
- Luxurious appearance with unique colors.
- Scratch and heat-resistant.
- Disadvantages:
- Expensive.
- Requires periodic maintenance (especially marble due to its susceptibility to staining).
- Advantages:
- Quartz:
- An artificial stone that combines beauty and durability.
- Low maintenance.
- Usage:
- Countertops.
1.6 Plastics and Composites
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride):
- Advantages:
- Water-resistant and easy to clean.
- Low cost.
- Disadvantages:
- Short lifespan.
- Not resistant to high heat.
- Advantages:
- Acrylic:
- Advantages:
- Shiny and modern look.
- Scratch-resistant.
- Disadvantages:
- Can deform under high temperatures.
- Advantages:
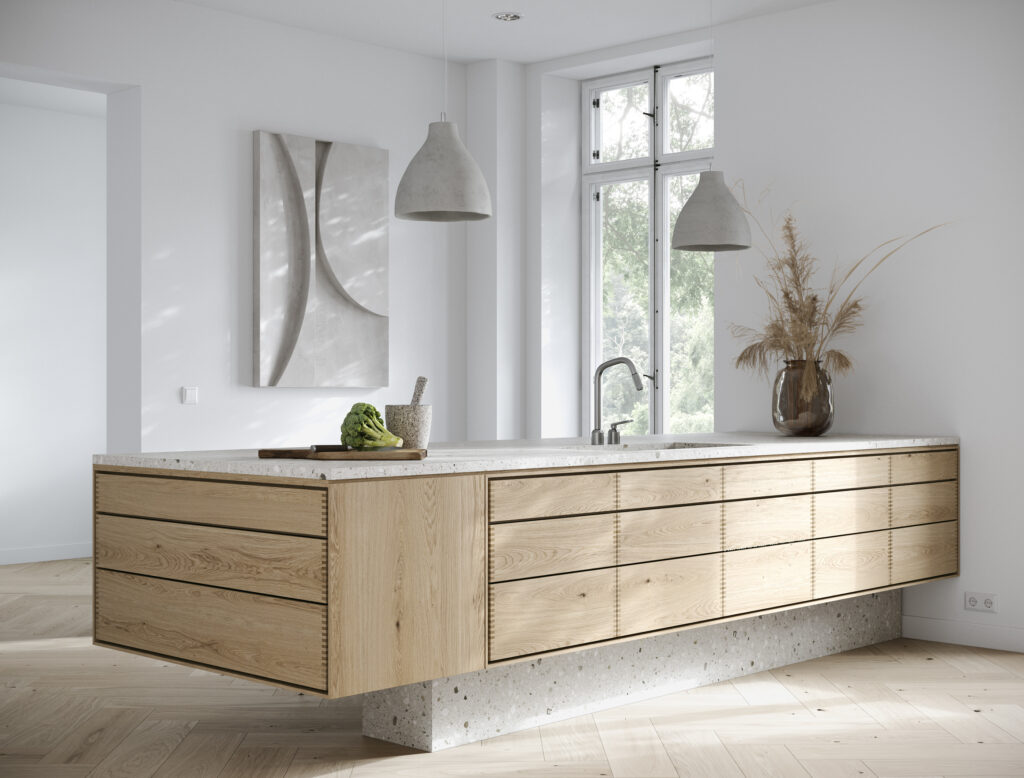

2. Choosing Suitable Materials Based on the Following Factors
2.1 Moisture
- Humid areas require water-resistant materials like stainless steel, PVC, or high-quality HDF.
2.2 Daily Usage
- For kitchens used frequently, choose durable materials such as granite or quartz for countertops and plywood for cabinets.
2.3 Budget
- Limited Budget:
- Use MDF or PVC.
- Moderate Budget:
- Plywood with water-resistant finishes.
- High Budget:
- Natural wood with natural stone countertops.
2.4 Aesthetics and Design
- Modern Kitchens:
- Metals, acrylic, glass.
- Classic or Rustic Kitchens:
- Natural wood, marble.
3. Additional Tips
- Ensure Quality Finishes: Use protective coatings (e.g., moisture-resistant paints) to prolong material lifespan.
- Choose Easy-to-Maintain Materials: Especially if you want to reduce cleaning time and effort.
- Balance Beauty and Functionality: Focus not only on appearance but also on materials that suit your daily needs.
By carefully selecting materials based on these guidelines, you’ll achieve a durable and attractive kitchen that lasts for years. If you need help designing your kitchen or choosing suppliers, feel free to ask!